Welcome to howtocivil.This comparative article will describe the basic difference between pipe flow and open channel flow based on their properties, flow, and nature. Before starting the main comparison between open channel vs pipe flow, you need to know what is an open channel flow and pipe flow. so let’s start
Open Channel Flow :
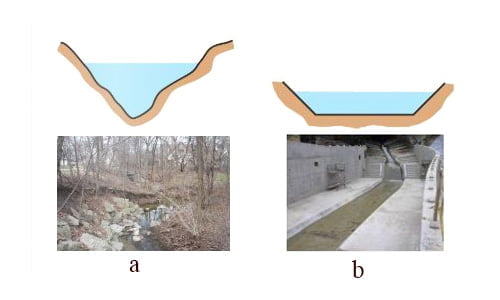
Open Channel Flow is a type of fluid flow in a conduit with a free surface open to the atmosphere.[1]
Examples: rivers, streams, floods, irrigation, Drainage ditches, etc. Having a free surface of a flow is not always an open channel flow. Such as flows of liquid at the Earth’s surface, like ocean-surface currents or rivers also not an open channel flow. The pressure and the shear stress are zero everywhere in the terms of boundary conditions at the free surface.[2]
Pipe Flow Definition
When a liquid (water) flows within a closed conduit then it’s called pipe flow. There is no free surface in this type of flow and also does not exert direct atmospheric pressure like open channel flow. But it exerts hydraulic pressure on the conduit. Like open Channel flow, not all flow within a closed conduit is pipe flow.
A comparative demonstration of pipe flow and open channel flow.
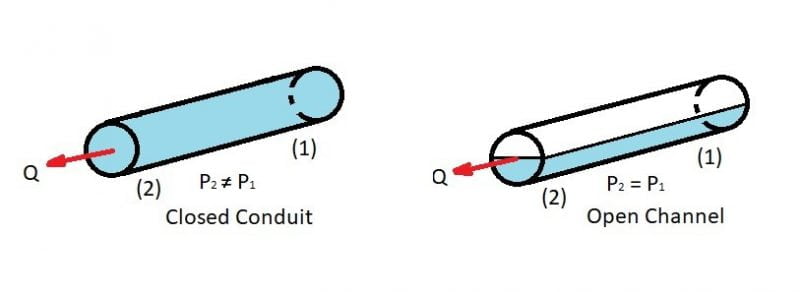
The basic Differences between pipe flow and open channel Flow are,
Pipe flow Vs Open channel Flow
| Open Channel Flow | Pipe Flow | |
| 1 | Open Channel Flow is a type of fluid flow in a conduit with a free surface open to the atmosphere. | The pipe flow is a type of flow within a closed conduit. |
| 2 | Open Channel Flow has a free surface | There is no Free surface in pipe flow |
| 3 | The pressure at the free surface remains constant | Pressure in the pipe is not constant |
| 4 | Flow Driven by Gravity | Flow Driven by Pressure |
| 5 | The maximum velocity occurs at a little distance below the water surface | The maximum velocity occurs at the center of the pipe. |
| 6 | Surface roughness varies with depth of flow | Surface roughness varies with the type of pipe material |
| 7 | HGL(Hydraulic Gradient Line ) coincides with the water surface line. | HGL(Hydraulic Gradient Line ) do not coincide top surface of the water |
| 8 | The Cross-section of an open channel can be trapezoidal, triangular, rectangular, circular, etc. | The Cross-section of a pipe generally circular. |
| 9 | 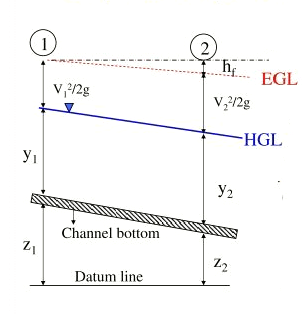 |
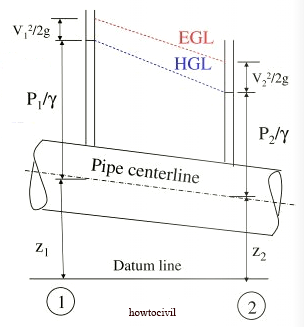 |
[epcl_box type=”information”]Reference : [/epcl_box]
- Open Channel Flow
- Open Channel Flow Lecture From MIT
- Open Channel slide
- Flow Simulation inside a pipe in Solidworks
If you like this article don’t forget to share it with your social media account and friends. Also if you have any questions regarding this pipe flow vs open channel article then please comments. thank you.









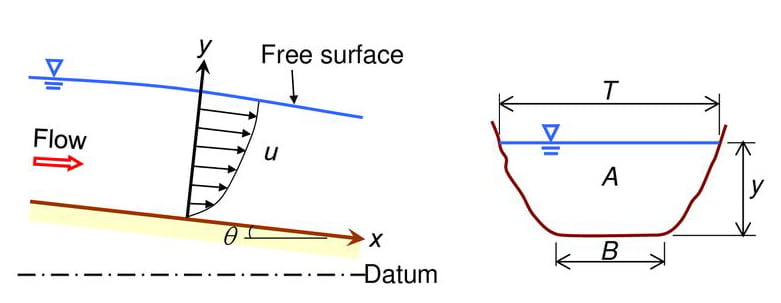
how will be the diagrams of velocity profile for both open and close channels?
Thanks For your Comment Umair! Attached the diagrams of velocity profile for both open and close channels.

which flow i will be say when pipe is not completely fill the cross section of pipe