Grillage foundations are a specialized type of foundation utilized primarily for heavy structures with large column loads. These foundations are designed to distribute the load evenly across the ground, reducing the risk of settlement and other structural issues. In this blog post, I will provide a comprehensive overview of grillage foundations, discussing their types, components, advantages, applications, and design considerations.
What is Grillage Foundation?
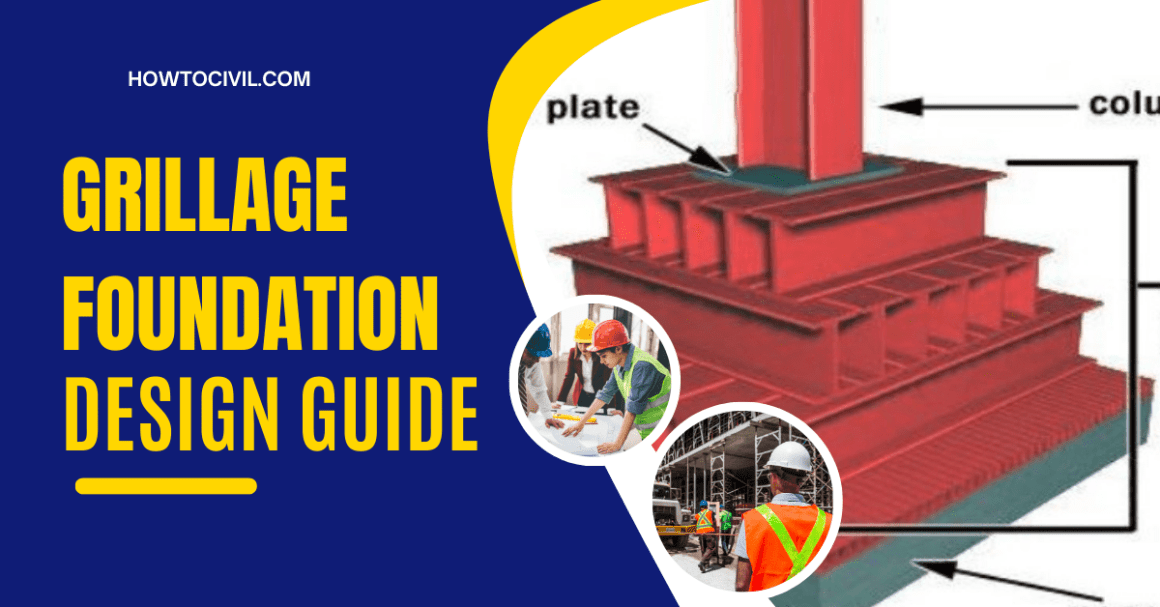
A Grillage foundation is a type of shallow foundation used to distribute heavy structural loads over a large area. It is commonly employed in constructing bridges, towers, or other heavy structures where the soil has a low bearing capacity. The loads must be spread out to avoid excessive settlement or failure. The foundation consists of one or more layers of steel beams, timber, or reinforced concrete beams, arranged in a grid-like pattern, which transfers the load from the structure above to the underlying soil.
The primary purpose of a grillage foundation is to provide a stable, load-bearing platform that distributes the structural loads evenly, reducing the risk of uneven settlement or soil failure. This type of foundation is beneficial in situations where traditional spread footings or piers may not be suitable due to the soil conditions, size of the load, or other factors.
Key Components of Grillage Foundation
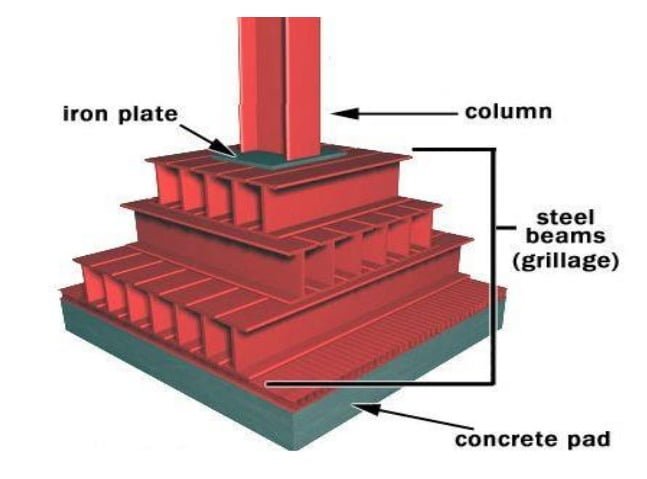
A typical grillage foundation consists of three main components: grillage beams, bearing plates, and concrete pedestals.
Grillage Beams
Grillage beams are horizontal structural members, typically made from steel or reinforced concrete, that are laid in one or more layers. These beams are connected perpendicularly to distribute the load from the superstructure to the ground. Steel beams are often preferred for their high strength-to-weight ratio, but reinforced concrete beams can also be used if required by the specific project.
Bearing Plates
Bearing plates are used to transfer the load from the columns to the grillage beams. They are typically made from steel and are designed to spread the load over a larger area, reducing the stress on the grillage beams and ensuring the foundation’s stability.
Concrete Pedestals
Concrete pedestals are placed beneath the grillage beams to provide support and distribute the load to the ground. They also act as a leveling agent, ensuring that the grillage beams are positioned at the correct height to maintain the overall stability of the foundation.
Types of Grillage Foundations
There are two main types of grillage foundations: steel grillage foundation and timber grillage foundation. Each type serves the same purpose of distributing loads over a larger area, but the choice between them depends on factors like the availability of materials, cost, and specific project requirements.
Steel Grillage Foundation:
Steel grillage foundations consist of steel beams or steel channels laid in one or more layers, typically in a perpendicular or crisscross arrangement. The steel beams are placed on a prepared bed of concrete or a layer of compacted granular material, depending on the soil conditions and design requirements. The structure’s columns or walls are then erected on top of the steel grillage, transferring the load to the beams, which in turn distribute it evenly over the underlying soil.
Steel grillage foundations offer several advantages, including high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion (when adequately protected). They are well-suited for heavy structures or situations where a high degree of load distribution is needed. However, steel grillage foundations tend to be more expensive than timber grillage foundations due to the cost of steel and the need for skilled labor for assembly.
Timber Grillage Foundation:
Timber grillage foundations consist of wooden beams or logs laid in one or more layers, also in a perpendicular or crisscross arrangement. Similar to steel grillage foundations, the timber beams are placed on a prepared bed of concrete or compacted granular material. The structure’s columns or walls are then constructed on top of the timber grillage, which transfers the load to the underlying soil.
Timber grillage foundations are generally more cost-effective and easier to construct than steel grillage foundations, particularly in areas where timber is readily available. However, they may not be suitable for very heavy structures, as the load-bearing capacity of timber is lower than that of steel. Additionally, timber grillage foundations may be more susceptible to decay and insect attack, which can compromise their long-term performance.
| Feature | Steel Grillage Foundation | Timber Grillage Foundation |
| Corrosion Resistance | Susceptible to corrosion | Not affected by corrosion |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Load-bearing Capacity | Higher | Lower |
| Ease of Installation | Moderate | Easier |
| Maintenance | Requires corrosion protection | Requires protection from decay |
| Environmental Impact | Higher embodied energy | Lower embodied energy, renewable |
| Fire Resistance | Higher, non-combustible | Lower, combustible |
| Response to Moisture | Not affected by moisture | Susceptible to moisture damage |
| Adaptability to Soil Movement | Less adaptable | More adaptable |
| Seismic Performance | Generally better | Generally lower |
It’s essential to consider the specific project requirements and site conditions when
Applications of Grillage Foundation
Grillage foundations are typically used for heavy structures that require a robust and reliable foundation system. Some common applications include:
Bridges and overpasses: Grillage foundations are ideal for supporting large, heavy loads and can accommodate the dynamic forces generated by traffic.
Transmission towers: These structures require strong and stable foundations to support the weight of the tower and electrical equipment.
Industrial structures: Grillage foundations are well-suited for heavy machinery and equipment foundations, providing a stable base for operation.
Design and Construction Considerations
When designing and constructing a grillage foundation, several factors must be taken into account to ensure the foundation’s effectiveness and longevity.
Load Calculation
Accurate load calculations are essential to determine the size, spacing, and configuration of grillage beams and bearing plates. These calculations should account for both the dead load (weight of the structure) and live load (additional forces due to occupancy, traffic, etc.).
Material Selection
Selecting the appropriate materials for the grillage beams, bearing plates, and concrete pedestals is crucial for ensuring the foundation’s structural integrity and longevity. Material selection should consider factors such as load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Structural Analysis
A thorough structural analysis should be conducted to ensure that the grillage foundation can adequately support the intended loads and resist the associated forces. This analysis may involve the use of computer modeling software to simulate various load conditions and assess the foundation’s performance under different scenarios.
Construction Techniques
Proper construction techniques are essential for ensuring the successful installation of a grillage foundation. Some key considerations include:
Site preparation:
Adequate excavation and soil compaction are necessary to provide a stable base for the concrete pedestals and grillage beams.
Beam placement:
Grillage beams should be placed at the appropriate spacing and depth to ensure even load distribution and structural stability.
Connection details:
Secure connections between the grillage beams, bearing plates, and columns are crucial for maintaining the foundation’s integrity and load transfer efficiency.
Step-by-step design procedures for grillage foundation are described in this attachment Design example of grillage foundation
also the verticle capacity is found (PDF) The vertical capacity of grillage foundations (researchgate.net)
Advantages of Grillage Foundation
Grillage foundations offer several advantages compared to other foundation types, making them an attractive choice for specific projects and site conditions. Here are some key advantages of grillage foundations in comparison to other foundation types:
- Shallow foundation: Grillage foundations are a shallow foundation type, which means they require less excavation and ground disturbance compared to deep foundations, such as piles or caissons. This can result in lower construction costs, reduced environmental impact, and faster construction times.
- Load distribution: Grillage foundations are designed to distribute heavy structural loads over a larger area, which can be particularly beneficial in areas with low bearing capacity soils or where traditional spread footings or piers might not be suitable.
- Adaptability: Grillage foundations can be designed to accommodate various soil conditions, structural loads, and project requirements. This flexibility allows them to be used in a wide range of scenarios where other foundation types might not be feasible or cost-effective.
- Ease of construction: Grillage foundations can be assembled relatively quickly compared to some other foundation types, as the beams can be prefabricated and installed on-site. This can lead to reduced construction time and lower labor costs.
- Material availability: In areas where timber is readily available, timber grillage foundations can be more affordable and environmentally friendly compared to other foundation types. Steel grillage foundations can also be a viable option when steel beams or channels are easily accessible.
- Aesthetic appeal: Timber grillage foundations can provide a natural and rustic appearance to a structure, which can be desirable in certain settings or architectural styles, setting them apart from other foundation types.
- Reduced settlement: Grillage foundations can help minimize differential settlement by distributing the structural loads more evenly across the underlying soil. This can be particularly beneficial in areas with compressible or uneven soil layers.
8. Improved durability: Steel grillage foundations, in particular, have a high resistance to corrosion, ensuring a long service life.
Limitations of Grillage Foundation
It is essential to consider these limitations when choosing a grillage foundation for a specific project. Working with experienced professionals and conducting a thorough site investigation can help ensure that the selected foundation type meets the project’s requirements and site conditions, ensuring long-term stability and performance,
However, Grillage Foundation has certain limitations that need to be considered when selecting the appropriate foundation type for a specific project:
- Soil conditions: Grillage foundations are suitable for soils with low bearing capacity, but they may not be the best choice for highly compressible or expansive soils, as these conditions can lead to uneven settlement or additional stresses on the grillage beams.
- Limited load-bearing capacity: While grillage foundations can support heavy structures, there is a limit to their load-bearing capacity. For extremely heavy structures or those with highly concentrated loads, other types of foundations, such as deep foundations, may be more appropriate.
- Susceptibility to environmental factors: Timber grillage foundations are more susceptible to decay, insect attack, and moisture-related issues than steel grillage foundations. Proper material selection, treatment, and maintenance can mitigate these risks, but they remain a limitation to consider.
- Cost and availability of materials: Steel grillage foundations tend to be more expensive than timber grillage foundations due to the cost of steel and skilled labor required for assembly. On the other hand, the availability of suitable timber species, sizes, and strengths may affect the feasibility of using a timber grillage foundation for a particular project.
- Installation complexity: Grillage foundations can be more challenging to install than other foundation types, such as spread footings, due to the need for careful alignment, leveling, and connections of the beams.
- Corrosion and protection: Steel grillage foundations are susceptible to corrosion if not adequately protected. This requires the use of protective coatings, galvanization, or other corrosion-resistant measures, which can increase the overall cost and maintenance requirements.
- Limited adaptability: Grillage foundations may not be suitable for sites with irregular or sloping topography, as they require a level and stable base for proper load distribution. In such cases, other foundation types may be more appropriate.
Step-by-step Construction Process of Grillage Foundation
The construction process of a grillage foundation involves several steps to ensure proper load distribution and long-term stability. Here is a step-by-step guide to constructing a grillage foundation:
- Site investigation and soil testing: Conduct a thorough site investigation to determine soil conditions, including bearing capacity, settlement characteristics, and groundwater levels. Soil tests, such as the Standard Penetration Test (SPT) or the Cone Penetration Test (CPT), can provide valuable data for the foundation design process.
- Foundation design: Design the grillage foundation based on the soil investigation results, structural loads, and project requirements. Calculate the size, spacing, and arrangement of the beams to achieve even load distribution and avoid excessive stress on any particular beam.
- Site preparation: Excavate the site to the required depth and remove any loose or unsuitable soil. Prepare a leveled and compacted bed of concrete or granular material, such as sand or gravel, to provide a stable base for the grillage foundation.
- Material procurement: Procure the materials required for the grillage foundation, such as steel or timber beams, channels, or logs. Ensure that the materials meet the required strength, durability, and corrosion or decay resistance specifications.
- Assembly of grillage beams: Arrange the beams or channels in one or more layers, typically in a crisscross or perpendicular pattern. The connections between the grillage members should be made using bolts, welding (for steel), screws, or traditional joinery methods (for timber).
- Beam leveling and alignment: Ensure that the grillage beams are properly leveled and aligned to provide an even surface for the structure above. This is crucial for proper load distribution and to avoid uneven settlement.
- Connection of grillage members: Securely connect the grillage beams at their intersections to create a stable and rigid grillage foundation. This can be done using bolts, welding (for steel), screws, or traditional joinery methods (for timber).
- Concrete or granular layer (optional): In some cases, a layer of concrete or granular material may be placed over the grillage foundation to further distribute the load and provide a suitable surface for constructing the columns or walls of the structure above.
- Waterproofing and protection (optional): Apply waterproofing and protective measures to the grillage foundation, if required. This can include applying protective coatings or membranes, installing drainage systems, or implementing other measures to protect the foundation from moisture and environmental factors.
- Erection of the structure: Construct the columns or walls of the structure on top of the grillage foundation, transferring the load to the foundation. Ensure that the load is evenly distributed across the grillage beams to prevent excessive stress on any particular beam.
- Quality control and inspection: Conduct regular quality control checks and inspections throughout the construction process to ensure that the grillage foundation is built according to the design specifications and meets the required performance standards.
By following these steps, a grillage foundation can be constructed to effectively distribute the structural loads over a large area and provide long-term stability and support for the structure it underpins.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers on grillage foundation
What is a grillage foundation?
A grillage foundation is a type of shallow foundation consisting of horizontal layers of beams (usually steel or wooden) laid on a layer of concrete or compacted soil. The beams are placed in a crisscross pattern to distribute the load evenly and reduce the pressure on the underlying soil. It is commonly used for supporting heavy structures like bridges, columns, and piers.
When should a grillage foundation be used?
Grillage foundations are suitable for situations where the bearing capacity of the soil is low, or when the structure’s load is concentrated on a few columns or piers. They are commonly used for bridges, heavy steel columns, tall chimneys, and towers.
What are the advantages of grillage foundations?
Some of the advantages of grillage foundations include:
-
- Ease of construction and relatively low cost
- Effective distribution of loads, reducing stress on the soil
- Suitable for a wide range of soil conditions
- Provides a stable base for heavy structures
- Reduces the risk of differential settlement
What are the main components of a grillage foundation?
A typical grillage foundation consists of the following components:
-
-
- A base layer (usually concrete or compacted soil) to provide a stable surface
- Horizontal layers of beams (typically steel or wooden) arranged in a crisscross pattern
- Concrete or grout filling the spaces between the beams to provide additional stability and load distribution
-
How do I design a grillage foundation?
Designing a grillage foundation involves several steps, including:
-
-
-
- Determining the load and load distribution from the structure
- Analyzing the soil conditions and bearing capacity
- Selecting appropriate materials for the grillage beams (usually steel or wooden)
- Calculating the size, spacing, and arrangement of the beams
- Ensuring proper reinforcement and connection between the beams It is recommended to consult with a structural engineer or geotechnical engineer when designing a grillage foundation for a specific project.
-
-
What are the disadvantages of grillage foundations?
Some of the disadvantages of grillage foundations include:
-
-
-
-
- Limited to shallow depths, making it unsuitable for deep foundations
- Susceptibility to corrosion or decay, depending on the material used
- Possible need for regular maintenance and inspection
- May not be suitable for soils with high water tables or excessive moisture
-
-
-
How do I maintain a grillage foundation?
Maintaining a grillage foundation involves periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure its continued performance and structural integrity. Some maintenance activities include:
-
-
-
-
-
- Regular visual inspection of the foundation for signs of corrosion, decay, or damage
- Checking for differential settlement or movement in the structure
- Ensuring proper drainage around the foundation to prevent water accumulation
- Applying protective coatings or treatments to the grillage beams, if necessary
-
-
-
-
How does a grillage foundation compare to other types of foundations?
Grillage foundations are a suitable option when dealing with low soil-bearing capacity and when supporting heavy structures with concentrated loads. While they are relatively easy to construct and cost-effective, they may not be the best choice for every situation. Other types of foundations, such as spread footings, pile foundations, or raft foundations, might be more appropriate depending on factors such as soil conditions, water table, structural loads, and construction constraints.
Are grillage foundations suitable for residential construction?
Grillage foundations are typically used for heavy structures like bridges, columns, and piers. However, they can be used in residential construction under certain circumstances, such as when the soil has low bearing capacity or when supporting a heavy structure like a masonry fireplace. It is essential to consult with a structural engineer or geotechnical engineer to determine if a grillage foundation is suitable for a specific residential project.
Can I use a grillage foundation in an earthquake-prone area?
Grillage foundations can be used in earthquake-prone areas, provided they are designed and constructed to accommodate the anticipated ground movements and stresses. This may involve using specific materials, reinforcement, or connections to ensure adequate performance during seismic events. It is crucial to consult with a structural engineer experienced in seismic design to determine the best approach for a project in an earthquake-prone area.
Grillage foundations are a versatile and robust solution for supporting heavy structures with large column loads. By distributing loads efficiently and accommodating a range of soil types and structural configurations, these foundations offer numerous advantages over other foundation types.
When designing and constructing a grillage foundation, careful attention must be paid to factors such as load calculation, material selection, structural analysis, and construction techniques to ensure the foundation’s success and longevity. As demonstrated by the case study, a well-designed and constructed grillage foundation can provide a stable and reliable base for even the most demanding structures.
References :
https://www.geoengineer.org/storage/publication/20490/publication_file/2746/EL-6965.pdf