Gypsum plaster, calcined plaster, or the Plaster of Paris is one of the most abundantly utilized materials globally. From the dawn of civilization to the postmodern era, gypsum plastering remains a common domain in construction and other industries due to its extraordinary properties and uses. The most common types of plastering techniques are Lime plastering, cement plastering, and gypsum plastering.
A typical new American household contains seven metric tons of gypsum(USGS,2020). An average person is surrounded by gypsum plaster and other derivative products from dawn to dusk, from the cradle to the grave, but most people don’t know. In this article, I will describe everything you need to know about gypsum plastering.

What is Gypsum Plaster?
Gypsum plaster is a type of white cementing material that is made by dehydration of the mineral gypsum. It is a finely powdered form substance chemically known as calcium hemihydrate (CaSO4.1/2H2O) and can easily be found in the market.
Historical Reference:
History is replete with the usage of gypsum plaster. It has been used through ancient times by Assyrians, Greeks, Egyptians, and in Paris. Old cuneiform scripts of the Assyrians are supposed to be written with gypsum plaster.
Greeks used it in their temples, and they were so much inspired by it that they had its name on the name of their moon goddess, “selenite.” It was because of its shining property like the moon.

Similarly, the Egyptians used gypsum plaster on the pyramids’ inside walls and palaces to increase their durability
Plaster of Paris got its name due to its large deposits in Paris. In 1666, a fire raged across London, destroying many parts of it, and in its aftermath king of France ordered gypsum plastering of wooden construction to avoid any burning.
Types of Gypsum Plaster
There are different types of gypsum plasters based on their functions and the amount of heat applied during production.
- Casting Gypsum Plaster
- Anhydrite gypsum plaster
- Hemihydrate gypsum plaster
- Finish Gypsum Plaster
- Undercoat Gypsum Plaster
- Machine applied Gypsum Plaster
- One Coat Gypsum Plaster
Difference between Gypsum and Plaster of Paris:
People often confuse gypsum plaster( plaster of Paris) with gypsum. However, they are way different from each other. ❝ Gypsum, a rocklike mineral known chemically as hydrous calcium sulfate (CaSO42H2O), is found in many parts of the world, usually combined with impurities such as limestone, clay, and iron oxides ❞ (M.G. Goyal,2002).
The cardinal difference between them is that gypsum is a naturally occurring white or colorless crystalline mineral found in sedimentary rocks. Still, plaster of Paris is a non-crystalline white-colored derivative of gypsum.
Properties of Gypsum Plaster:
Gypsum plaster is lightweight and hence does not put a structural load on buildings. Its molecules occupy a definite arrangement after setting; therefore, it does not shrink hardening processes, unlike cement plaster. It is less prone to cracks because the particles are bound with each other. It is due to less amount of water in it, unlike gypsum.

Gypsum is non-combustible due to the presence of content of crystal water. In the event of a fire, it protects the blockwork, concrete, and steel. It prevents rusting of metal fittings like pipes and increases their durability. Gypsum plaster has a low thermal conductivity value of 0.00261 gm. cal./sec./deg C./cm that’s why it ensures energy and power saving. It gives high tensile (LPOP and CPOP are 148 and 460 N) and flexural strength used in composite material production.
How Is Plaster Of Paris Chemically Different From Gypsum?
Other than different physical properties, both substances are also chemically different. Gypsum contains two crystallization water ( dihydrate) water molecules. It means two water molecules surround a single calcium sulfate molecule. It makes water to approximately 20% by mass. However, Plaster of Paris is a hemihydrate compound, which means it contains half molecule of water in its structure.
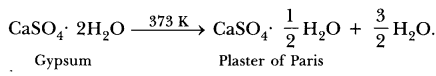
It is formed when gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) calcium sulfate dihydrate loses its crystallization water through calcination. ( Walter Scarborough et al.,2012)
CaSO4·2H2O + heat → CaSO4·0.5H2O + 1.5H2O (released as steam).
Prices Of Gypsum Plaster In India And USA
Following are the few quotations of gypsum plaster in India and the USA :
- Prices In India:
Powder Gypsum Wall Plastering= INR 5900/ metric ton
White Super Fine Plus Gypsum Plaster=INR 90/ bag
- Prices In the USA:
Calcined gypsum= USD 30/ metric ton
Uses of Gypsum Plaster:
Plaster of Paris has been used in building and architecture for centuries. Its been used primarily for decorative purposes, such as 16th-century monuments that exhibit art and culture ( Sistine chapel building roof decorated by Michelangelo). It is still being used nowadays for ceilings and wall coating as it provides an aesthetic touch so widely being used in interior design.

Plaster of Paris is also being used in sculpting (one might have seen beautiful statues of Buddha ), mold making for industrial use, and 3D printing that has become very popular in this era. Moving towards medicinal use, it is a perfect material for soft bandages and treating fractures (Borrelli J. et al.,2006).

Advantages and Disadvantages of Gypsum Plastering :
Like any other substance, plaster of Paris also possesses some advantages and disadvantages; however, its benefits consistently exceed its misfits.
Advantages of plaster of Paris are:
- It has no appreciable chemical action on paints and does not cause an alkali attack.
- Tiles and blocks of plaster of Paris are light and fire-resistant.
- Plaster of Paris provides the right decorative
- It is lightweight and has more durability.
- It has low thermal conductivity.
- It is terrific fire resistant and hence an excellent thermal insula
- It is not affected by any insects also does not favor the growth of fungus.
Disadvantages of plaster of Paris are:
- It is slightly soluble in water; therefore, it cannot be used in exterior design.
- More costly than other plasters, therefore, becomes uneconomical.
- It needs skillful personnel to handle it; therefore becomes expensive.
By summarizing, it can be said that gypsum plaster or plaster of Paris is a fine powder substance that hardens on mixing with water to provide a compact finish.

It is being used for millennia by almost every great civilization. It has magical properties that differentiate it from other plasters. Hence, its uses are plethora ranging from decoration, architecture, medicine, molding to 3D designs, etc.
[epcl_box type=”information”]References:[/epcl_box]
- Neville A.M. (2013). Properties of concrete. 5thedition, Dorling Kindersley India Pvt. Ltd.
- M.S. Shetty (2005) Concrete Technology Theory and Practice. Sixth Edition, New Delhi, S.Chand & Company Ltd.
- S. K. Duggal (2008) Building Materials Third Revised Edition. New Delhi, New Age International (P) Limited.
- Mclanahan,( 2019, Jan) https://www.mclanahan.com/blog/five-things-you-didnt-know-about-gypsum
- Crangle,Robert(2020)https://www.usgs.gov/centers/nmic/gypsum-statistics-and-information#:~:text=Most%20gypsum%20in%20the%20United,metric%20tons%20of%20gypsum%20alone.&text=Gypsum%20also%20is%20used%20extensively,well%20as%20in%20agricultural%20regions.
- www.facebook.com/gypsumplastering